(a) No person may begin a flight in an airplane under VFR conditions unless (considering wind and forecast weather conditions) there is enough fuel to fly to the first point of intended landing and, assuming normal cruising speed— (1) During the day, to fly after that for at least 30 minutes; or (2) At night, to fly after that for at least 45 minutes.. Make sure your simulator/aircraft are also in KG. If they are in LBS and you enter the KG figure, you'll end up with half as much fuel as required. Make sure you match SimBrief's ZFW with the actual aircraft ZFW in the sim. Heavier aircraft burn more. Make sure you're cruising at or close to the same altitude and speed as planned.

PPT Fire Investigation PowerPoint Presentation ID2354711

Spontaneously Combustible Class 4 Placard K5628 by
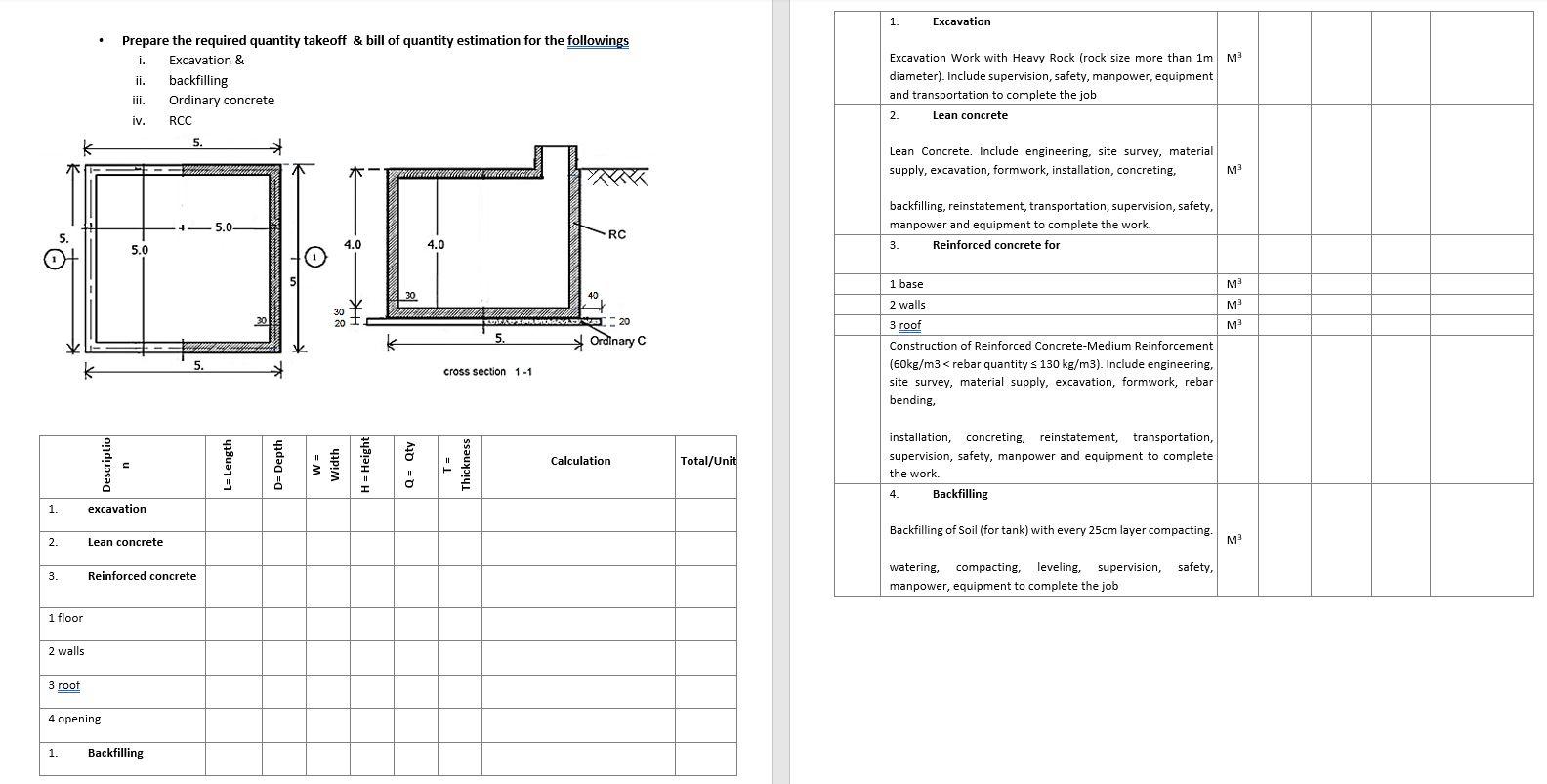
Solved 1. Excavation Prepare the required quantity takeoff &

Combustion Air HVAC School

PPT VENTILATION SYSTEM PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
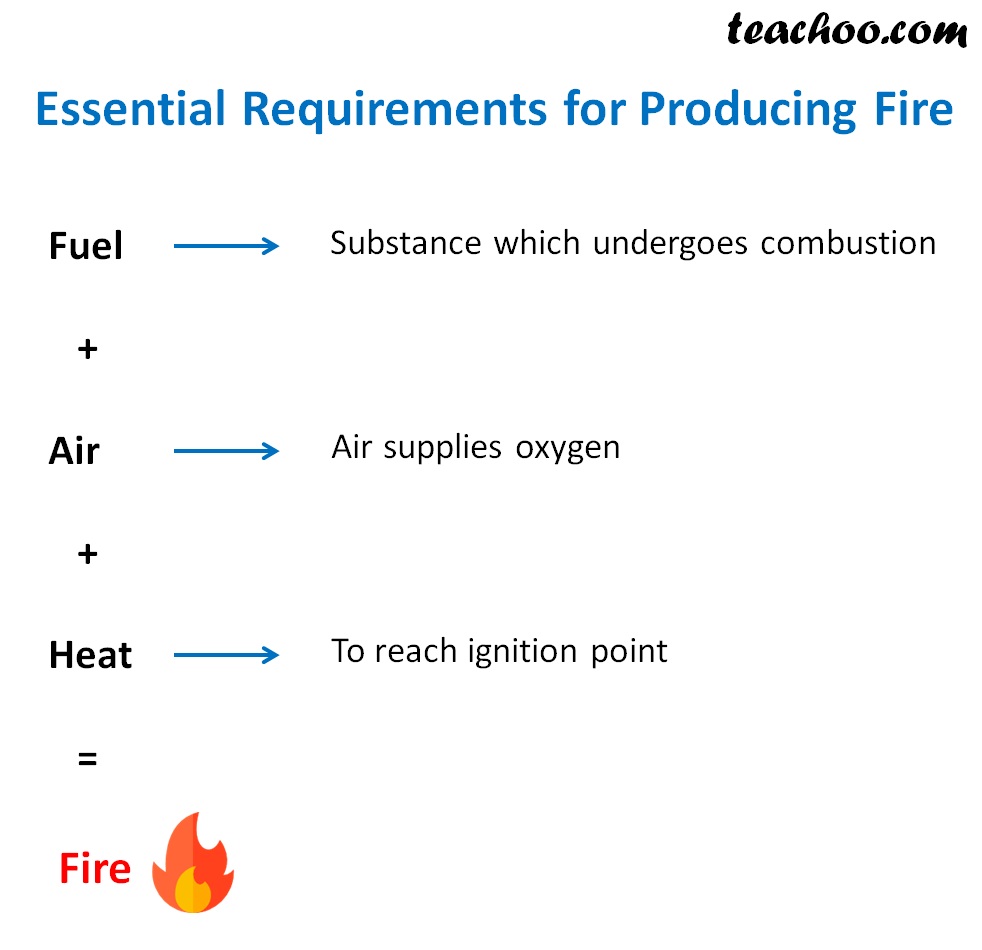
Conditions Necessary for Combustion Chapter 6 Class 8 Science Notes
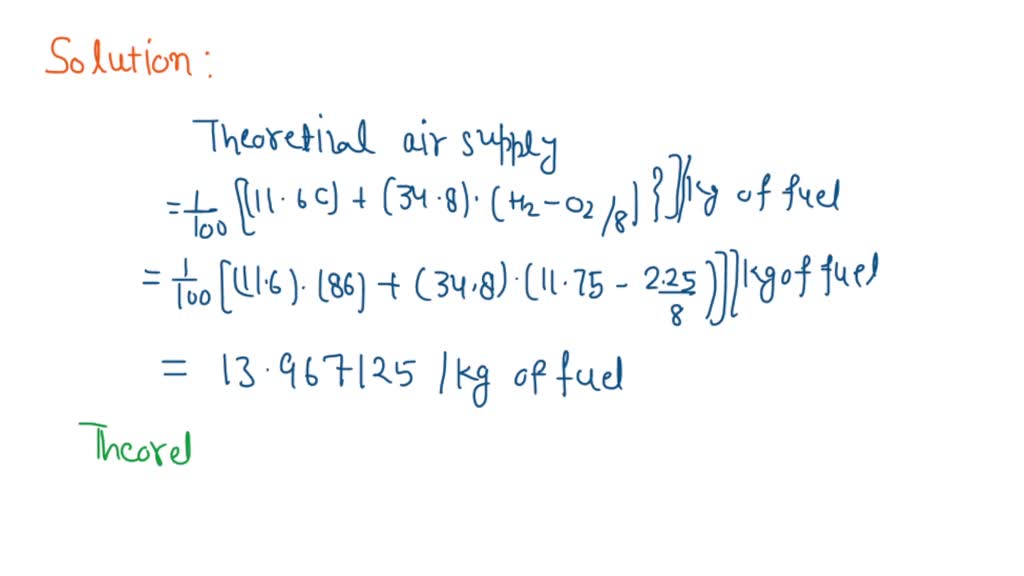
SOLVED A fuel has the following composition by weight Carbon = 86

Facing a Combustible Dust Hazard? Consider These Three Questions
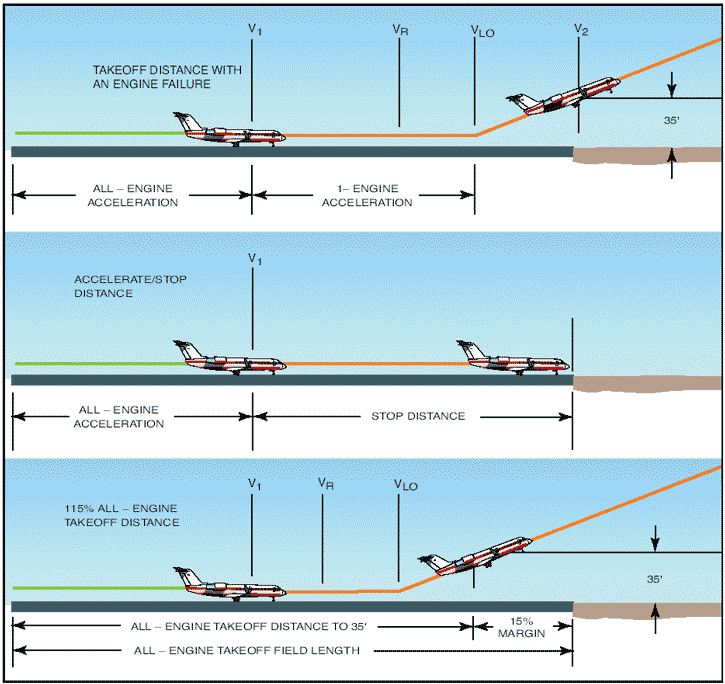
CRM Aviation Human Factors & Safety Pilot Guide to Takeoff Safety

High temperature storage criteria for combustible liquids Download Table
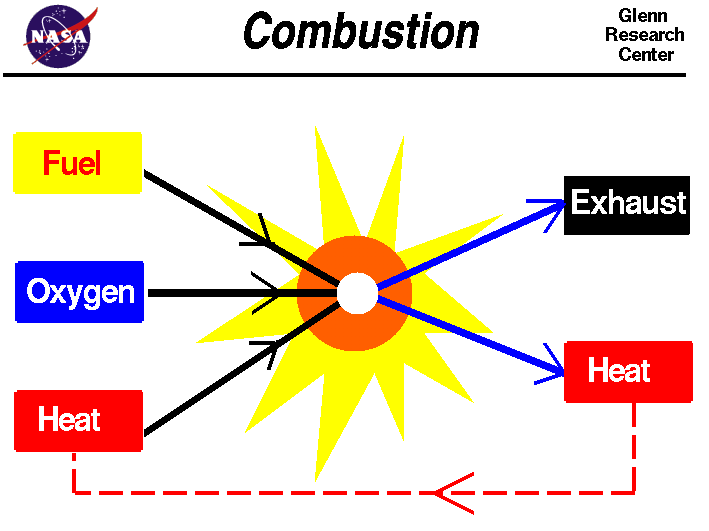
Combustion

TAKEOFF PERFORMANCE TAKEOFF CONSIDERATIONS Factors to Consider Aircraft

PPT Flammable and Combustible Liquids PowerPoint Presentation, free

Combustion air requirements YouTube

lift Derivation of the Takeoff equation Aviation Stack Exchange
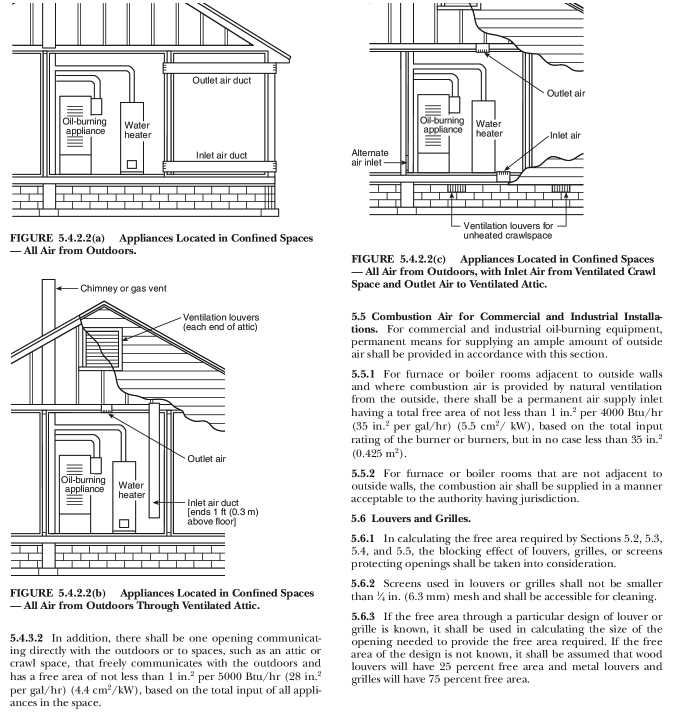
Combustion Air Requirements InterNACHI Inspection Narrative Library
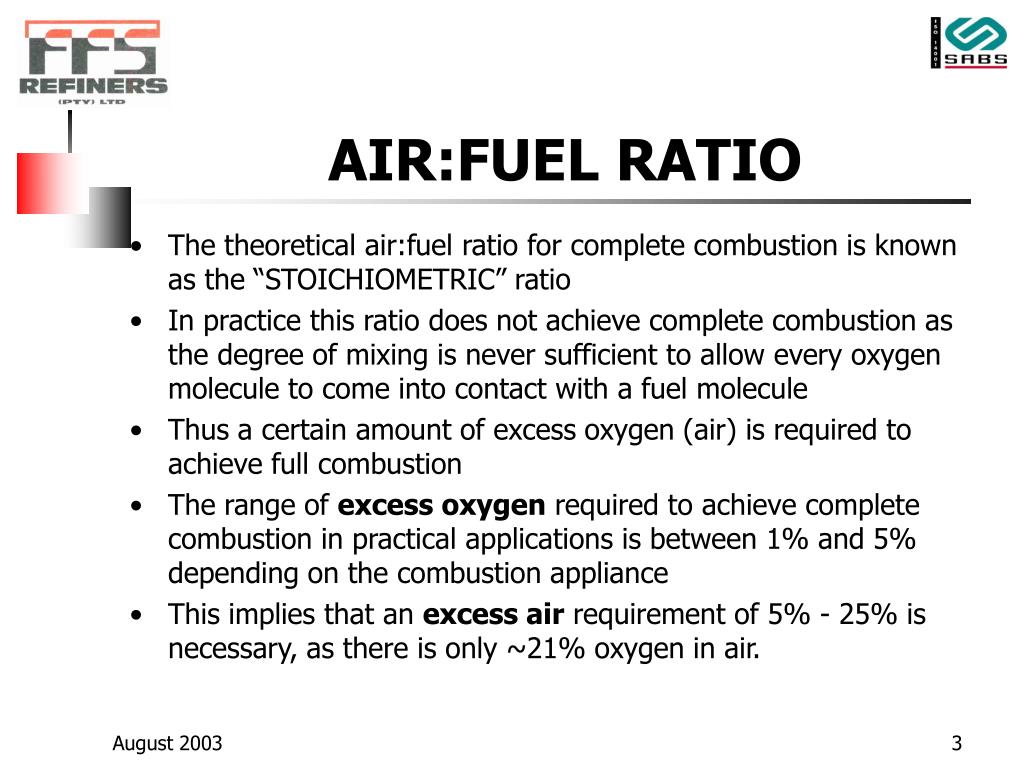
PPT COMBUSTION EFFICIENCY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

Separation of combustible material from masonry flues or fireplaces LABC
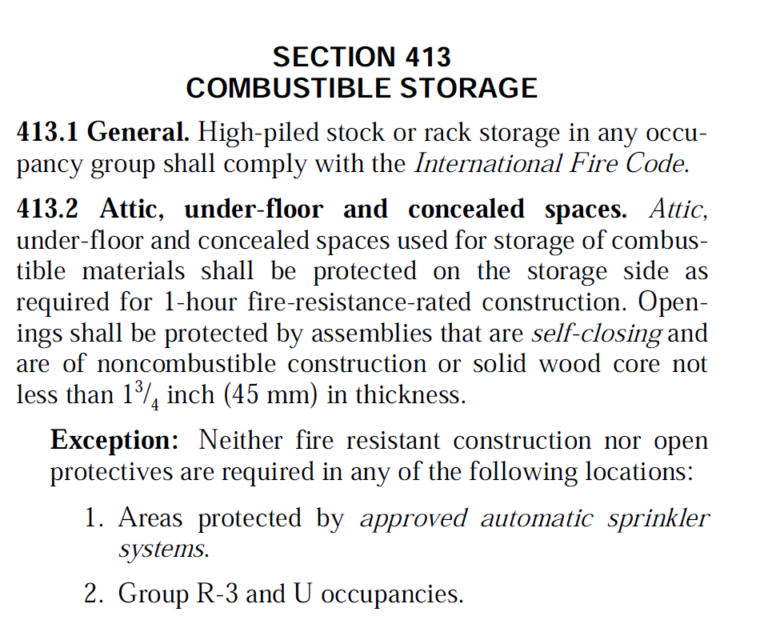
HighPiled Combustible Storage Common Special Requirements John P

Flammable Requirements Nfpa Review Home Decor
An F/A-18 taking off from an aircraft carrier An Embraer E-175 taking off. Takeoff is the phase of flight in which an aerospace vehicle leaves the ground and becomes airborne. For aircraft traveling vertically, this is known as liftoff.. For aircraft that take off horizontally, this usually involves starting with a transition from moving along the ground on a runway.. The zero-fuel weight (ZFW) of an aircraft is the total weight of the airplane and all its contents, minus the total weight of the usable fuel on board. Unusable fuel is included in ZFW. Remember the takeoff weight components contributions: + + = Where OEW is the Operating Empty Weight (that is a charactersitic of the plane), PL is the Payload actually embarqued, and FOB the Fuel actually.